GEOL2019DEBONE30636 GEOL
Newly discovered old volcano in Big Bend National Park
Type: Graduate
Author(s):
Kristin DeBone
Geological Sciences
Tamie Morgan
Geological Sciences
Advisor(s):
Richard Hanson
Geological Sciences
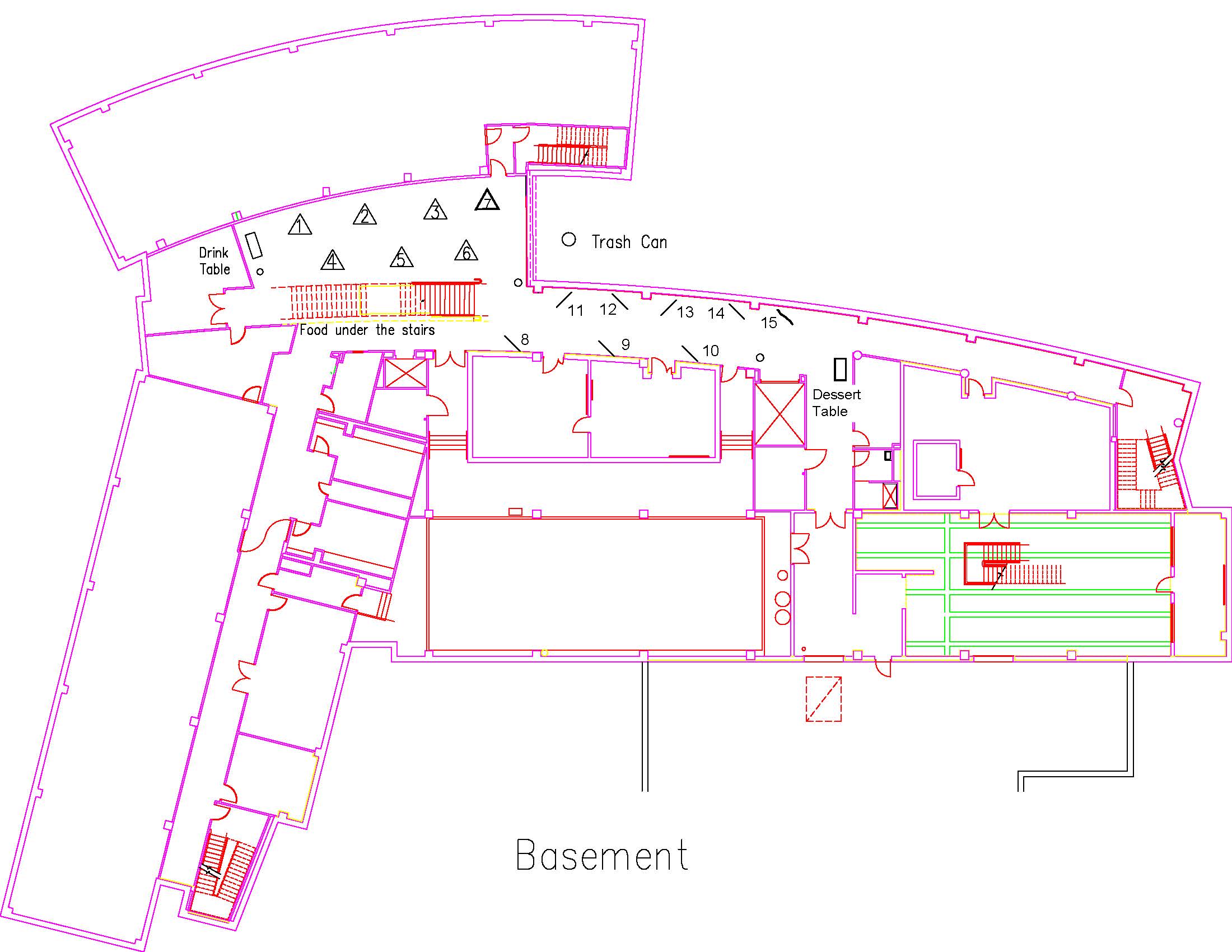
Location: Session: 2; Basement; Table Number: 8
(Presentation is private)Recent field work has discovered a volcanic complex within the Paleocene Black Peaks Formation in the northwestern part of Big Bend National Park in west Texas. This is the only known Paleocene volcano in west Texas. We have identified pyroclastic deposits consisting of ash-sized and coarser clasts, including volcanic bombs and blocks, which were erupted explosively from a nearby vent. Margins of the volcanic complex have been mapped using remote sensing because the volcanic rocks are distinctly different in color from the adjacent shale. Characteristics of the pyroclastics suggest derivation from phreatomagmatic eruptions, which occurred when magma and groundwater violently interacted in the shallow subsurface.
GEOL2019DONAHOO65357 GEOL
Using Non-Invasive Geophysical Techniques in Near-Surface Infrastructure and Agricultural Planning and Management
Type: Graduate
Author(s):
Michaela Donahoo
Geological Sciences
Advisor(s):
Omar Harvey
Geological Sciences
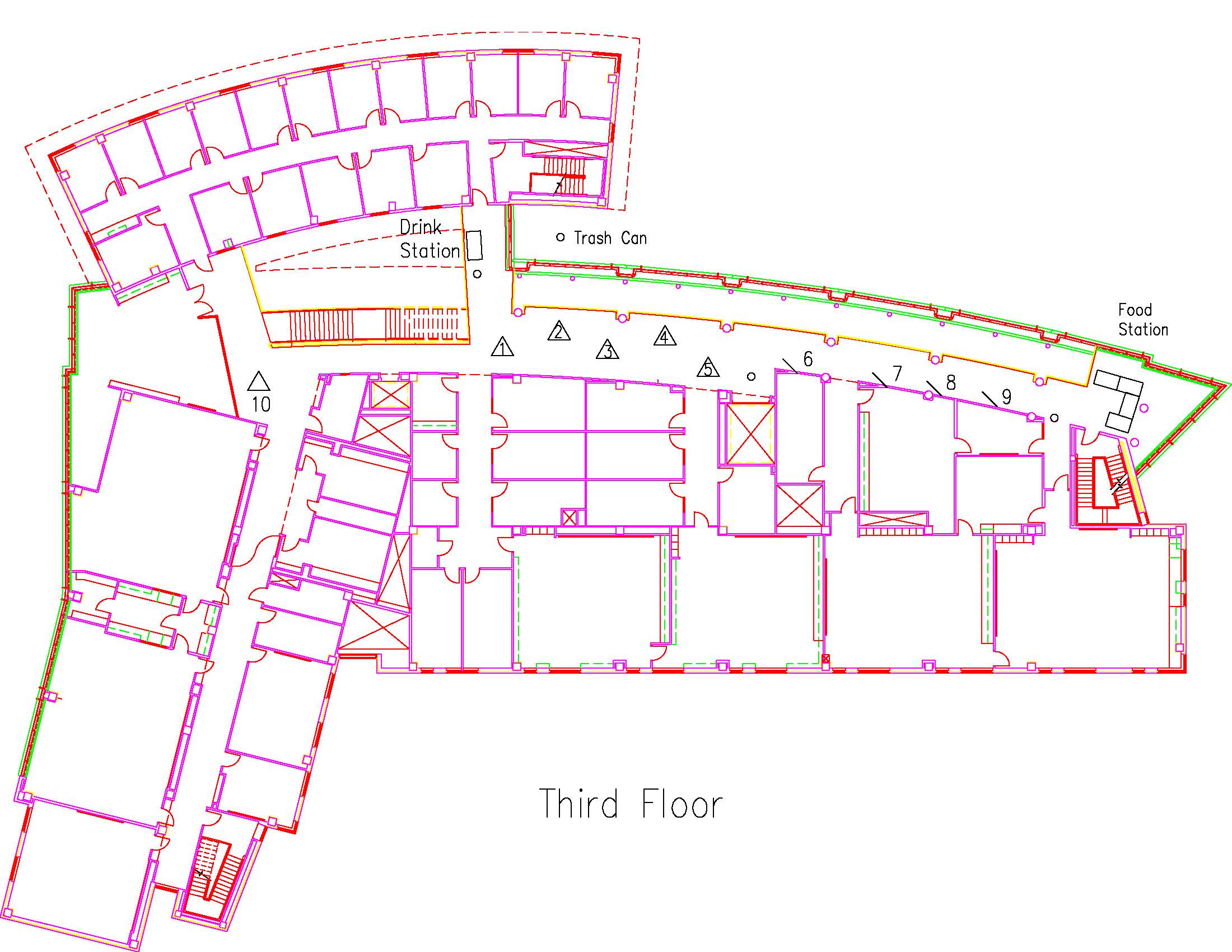
Location: Session: 2; 3rd Floor; Table Number: 7
View PresentationUsing Non-Invasive Geophysical Techniques in Near-Surface Infrastructure Planning and Management
Michaela Donahoo1, Karim Ouamer-ali2,3, Youcef Daoud2, Kaddour Djili3, Omar R. Harvey1
1Department of Geological Sciences, Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, Texas, USA.
2 National Institute of Agronomic Research of Algeria (INRAA), El-Harrach, Algeria.
3Ecole Nationale Supérieure Agronomique (ENSA), El-Harrach, Algeria.Understanding soil characteristic variability geospatially as a function of depth and time is key to the optimal implementation of subsurface infrastructure planning and expansion. The soils physical behavior as well as its interaction with piping and road materials determine where such a system could divert and predict future maintenance frequency. Central to the development of site-specific, precision management strategies is the quantification and mapping of the geospatial variability in soil properties at significantly higher resolutions than provided in current soil surveys. The presentation will cover results from ongoing collaborative research efforts between researchers at Texas Christian University and two Algerian institutions in using non-invasive measurements of bulk apparent electrical conductivity (ECa) to quantify and map 3-D soil variability in semi-arid and arid areas of Algeria, Northern Africa. The focus will be on the derivation and application of depth-specific ECa-ECe (saturated paste), ECa-clay content and ECa-water content relationships for use in understanding seasonal salinity and water dynamics within potential depths of construction interest.
GEOL2019LAMB52985 GEOL
A Source to Sink Analysis of the Dockum Group in the West Texas Highplains
Type: Graduate
Author(s):
Grayson Lamb
Geological Sciences
Advisor(s):
John Holbrook
Geological Sciences
Location: Session: 1; 3rd Floor; Table Number: 9

(Presentation is private)The fundamental understanding of any geologic basin stems from ascertaining the relationship between its source and sink. Every basin is therefore identified as a “sink” and has a provisional “source.” The investigation of this fundamental relationship is the preliminary exploration step to further basin development.
The Late Triassic Dockum Group of the west Texas high plains is an understudied group that begs investigation into the source to sink relationship. A comprehensive study of the Dockum Group as a “sink” is here undertaken in order to better understand the paleoclimate and its implications on the Dockum group depositional style. This study focuses on the northern most section of the Dockum group outcrop system. Within the study area it is subdivided into three main formations, the Tecovas mud, Trujillo sand, and Cooper Canyon sand-mud mix system.
This study showcases a forward stratigraphic modeling software, Dionisos Flow. From field based outcrop work: grain size, channel thickness, water discharge, and lithofacies assemblages were quantified as model inputs in Dionisos Flow.
The study aims to model Dockum Group sedimentation in order to determine the plausible paleoclimate, and its related depositional environment and depositional style. To do so, an outcrop study and fluvial architecture analysis was completed to serve as model input variables. Then a forward stratigraphic Dionisos Flow model of the three main Dockum Group formations was generated. It was then analyzed and coupled with the outcrop study to draw conclusions on the necessary Triassic climate conditions to produce the Dockum Group deposits.
Per the modeling exercise and outcrop study it is concluded that the Triassic climate was highly variable, shifting between semi-arid to humid. Its variability has been underemphasized in previous studies. Climate alterations are on a scale of 103 years. Additionally, the Dockum Group’s sedimentation style has been a forum of contradicting theories. This study has concluded that Dockum sands were deposited in a predominantly upper flow regime environment during humid climate cycles, while its abundant muds were deposited in lower flow during semi arid climate cycles.
GEOL2019LAURENTI12129 ENSC
Energetics and Bonding Dynamics in Amino and non-Amino Organic Molecules and Iron Oxides
Type: Graduate
Author(s):
Alec Laurenti
Environmental Sciences
Advisor(s):
Omar Harvey
Geological Sciences
Location: Session: 1; Basement; Table Number: 13

(Presentation is private)Iron oxides have a controlling effect on how carbon and contaminants move through the which has impacts on climate change and pollution. Carbon held more tightly to the soil can be sequestered for longer periods of time. These tightly held contaminants are less of a threat to spread and impact groundwater. The driving factor in the movement of these compounds are the binding-debinding energies. This study will use flow adsorption microcalorimetry to systematically analyze the energetics and bonding dynamics involved in different combinations of iron oxides and organic molecules of varying carbon chain lengths (along with the presence of amine functional groups). This will allow us to isolate the effect that these different chain lengths have as well as the presence of amine functional groups. The study will focus on the systematic collection and analysis of experimental data that can be used to support the development, validation, and refinement of computational models of interactions involving natural organic matter at the metal oxide-water interface while facilitating the further development of experimentally-driven understandings of binding-debinding dynamics of organic molecules onto mineral surfaces.
GEOL2019MIRKIN10373 GEOL
Background Color Matching in Texas Horned Lizards
Type: Graduate
Author(s):
Stephen Mirkin
Biology
Advisor(s):
Tamie Morgan
Geological Sciences
Location: Session: 2; Basement; Table Number: 1

View PresentationTexas horned lizards are a threatened species in the state of Texas with declines attributed to a variety of factors including: habitat conversion, pesticide use and red imported fire ants. These cryptic lizards in their natural habitats utilize a variety of anti-predator defense mechanisms. The primary defensive adaptation to avoid predators is often cited as their cryptic coloration, which is often suggested to color match the background substrates of the regions where they are found. Although background color-matching is purported to be an important factor in horned lizard defensive strategies it has never been empirically tested. Here we present the first known study of background color matching of Texas horned lizards in the state of Texas. We used a GIS analysis using soils and satellite imagery data to test how well Texas horned lizards match the soils and substrate in different regions of Texas.