BIOL2019TRULY25617 BIOL
Inducing Oxidative Stress Using Biotin Receptor Targeted Organometallic Compounds on Cancer Cells
Type: Undergraduate
Author(s):
Tate Truly
Biology
Advisor(s):
Giridhar Akkaraju
Biology
Kayla Green
Chemistry & Biochemistry
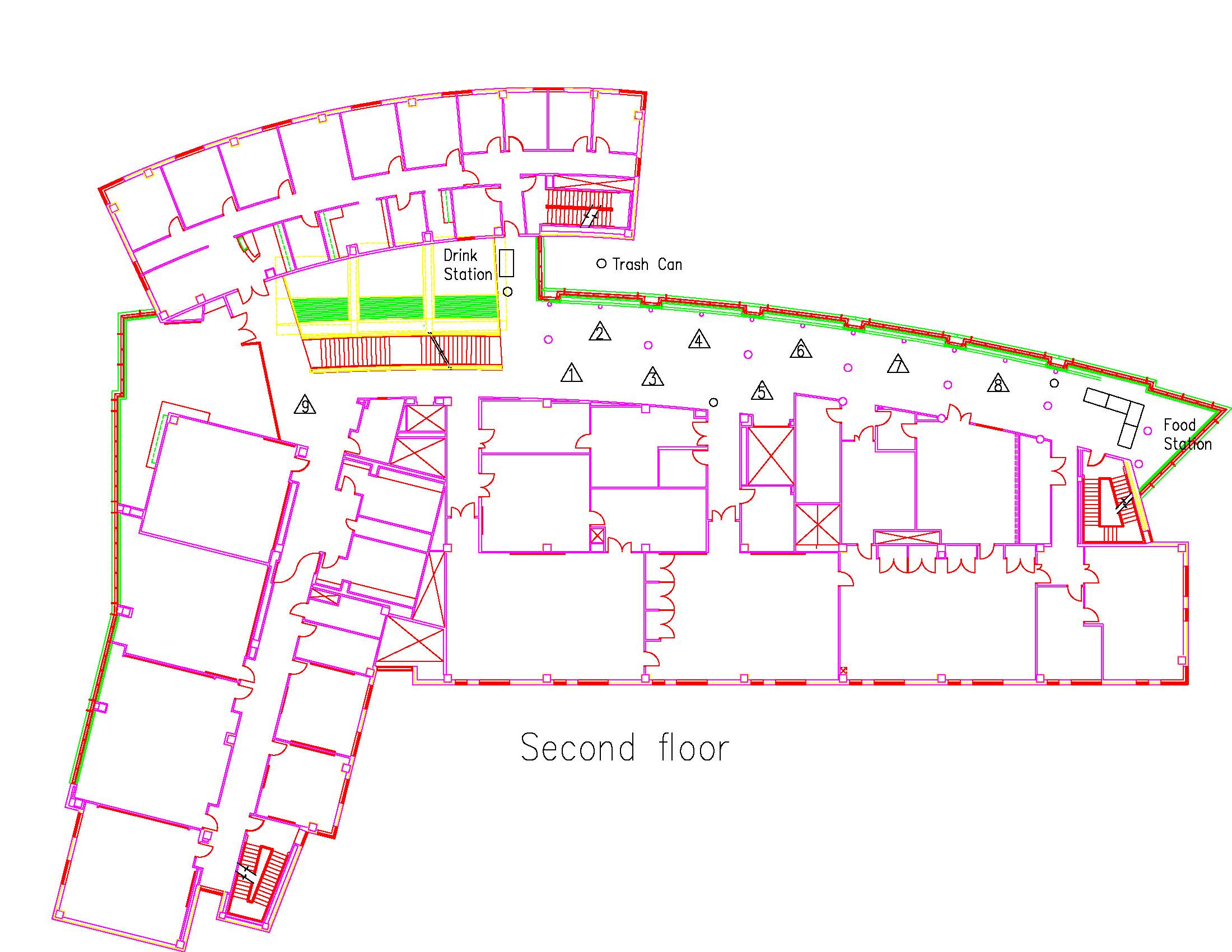
Location: Session: 2; 2nd Floor; Table Number: 5
View PresentationCancer is one of the leading causes of death in the United States and is predicted to directly affect 38% of the population over the course of their life. Cancer is categorized as a collection of diseases primarily characterized by aberrant cellular proliferation. Many current cancer therapies, such as chemotherapy, do not differentiate between cancer cells and normal cells resulting in a variety of negative side effects. In an attempt to minimize these side effects, there has been a huge impetus to develop targeted therapies, which exploit cancer-specific molecules to exhibit selective toxicity towards cancer cells. For example, the monoclonal antibody Trastuzumab (Herceptin) targets the Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) that is overexpressed in some breast cancer cells. Another cancer-specific molecule overexpressed in some breast cancers, as well as cervical cancers, is the receptor for biotin. Biotin, more commonly known as Vitamin B7, functions intracellularly as an important coenzyme for several carboxylase enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis, amino acid metabolism and gluconeogenesis. Thus, by overexpressing the biotin receptor some cancers increase their overall absorption of biotin resulting in a higher metabolic and proliferation rate. Furthermore, the high metabolic rate in cancer leads these cells to have increased to damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS) which can trigger apoptosis at high intracellular levels. Therefore, our project is exploring this overexpression of the biotin receptor as a potential avenue for targeted therapy against certain breast cancers. Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with an iron-center that has been shown to generate ROS in cancer cells. Since certain breast cancers overexpress the biotin receptor and absorb biotin with a higher efficiency, we hypothesize that conjugating biotin to ferrocene will increase the efficiency of ferrocene entering cancer cells, resulting in selective toxicity. Therefore, we have produced a library of biotin-ferrocene conjugates to test their ability to selectively enter cancer cells and generate ROS. Experiments were conducted utilizing ferrocene and a variety of conjugates (C1, C2, C3, 2) in both cancer (MCF-7) and non-cancer cells (HEK293).
BIOL2019WADE5244 BIOL
Exploring the Endocrine Activity of Nitrate: Does Exposure Alter Hormone Levels and Reproduction in Adult Fathead Minnows?
Type: Undergraduate
Author(s):
Caroline Wade
Biology
Hannah Nettelblad
Biology
Advisor(s):
Marlo Jeffries
Biology
Location: Session: 2; 2nd Floor; Table Number: 5

(Presentation is private)Endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) interfere with hormone production and action. EDCs typically mimic native hormones and often have a similar structure to natural hormones. While previous animal studies suggest that nitrate alters the synthesis of testosterone, nitrate is different than typical EDCs as its structure is not similar to that of any naturally occurring hormones. Given this and the environmental prevalence of nitrate, the objectives of this study are to 1) determine if nitrate acts as an EDC and 2) to better understand the mechanisms and effects of nitrate exposures on hormone production and reproduction. To achieve these objectives, groups of sexually mature adult fathead minnows were exposed to nitrate for 28 days. On days 7 and 28 of the exposure period, minnows were sacrificed for the collection of blood and gonads. The blood was used to evaluate hormone levels, while the gonads were used for gene expression analysis. Additionally, during the exposure, endpoints indicative of reproductive capabilities were also evaluated. There were no significant differences between exposure groups regarding gene expression, and there were no dose-dependent differences in egg production over the course of the breeding study.
CHEM2019BLITCH45678 CHEM
Strong Hydrogen Bonds to Weak Bases: An Orbital Overlap Perspective
Type: Undergraduate
Author(s):
Alexandra Blitch
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Advisor(s):
Benjamin Janesko
Chemistry & Biochemistry
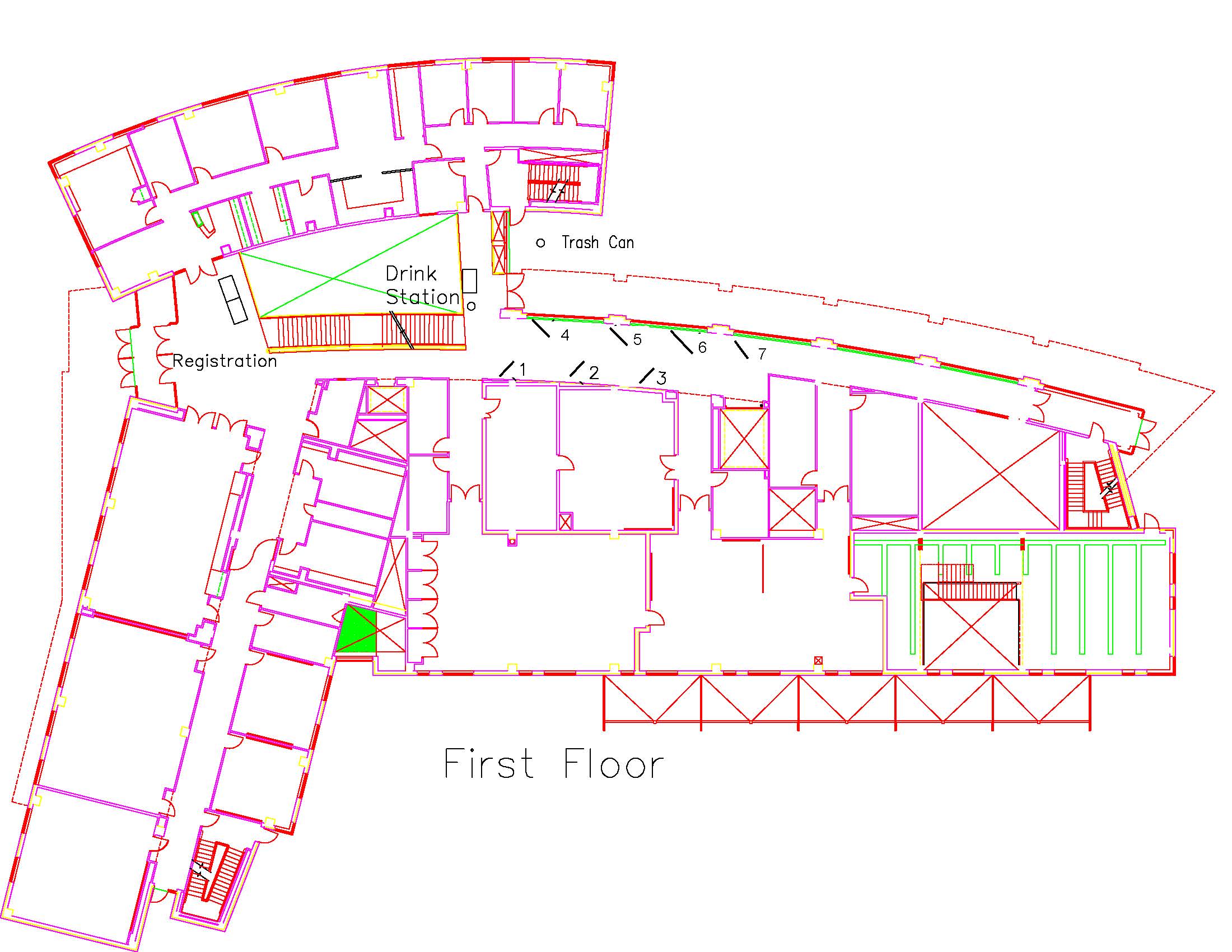
Location: Session: 2; 1st Floor; Table Number: 7
View PresentationIon solvation is fundamental in biochemistry. It controls the biophysical processes of protein solubility, reactivity, phase separation, crystallization and informational equilibria involving proteins and polypeptides. Ion solvation depends on the solute-solvent interactions which are governed by the properties of solvent like polarity, hydrogen bonding and ability to donate or accept electrons. These properties are subject to Pearson’s hard–soft acid–base (HSAB) effect and are characterized as hardness and softness of solvents. There have been attempts to connect the solvent hardness-softness to molecular properties and some empirical scales have been devised like μ-scale, DS scale and difference between the IR wavenumber shift of the C-I stretch of ICN and the O-H stretch of phenol. Only limited attempts have been reported to correlate the properties of solvents obtained from quantum chemical calculation to these empirical scales of solvent hardness-softness.
Our new quantum chemical descriptor, Orbital Overlap Distance, D(r), measures the size of orbital lobes that best overlap with the wavefunction around an atom. Compact, chemically stable atoms in the molecule tend to have overlap distances smaller than chemically soft, unstable atoms. Plots of D(r) on computed molecular surfaces, like electron density or spin density, distinguishes and quantifies the chemically soft and hard regions of a molecule. We propose that D(r) can be considered in terms of HSAB theory in order to predict solvation of ions. Our initial studies exhibit that D(r) of many common solvents correlates well with Marcus’s empirical μ-scale of solvent softness. Our studies provide a direct method to estimate the softness-hardness of solvents by using standard quantum chemical calculations.
CHEM2019BUCKINGHAM30657 CHEM
The Effects of Microgravity on the Creation of Nylon 6-10
Type: Undergraduate
Author(s):
Allison Buckingham
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Keira Clotfelter
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Jack Dietz
Biology
Tommy Gifford
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Waylan Kisor
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Advisor(s):
Magnus Rittby
Chemistry & Biochemistry
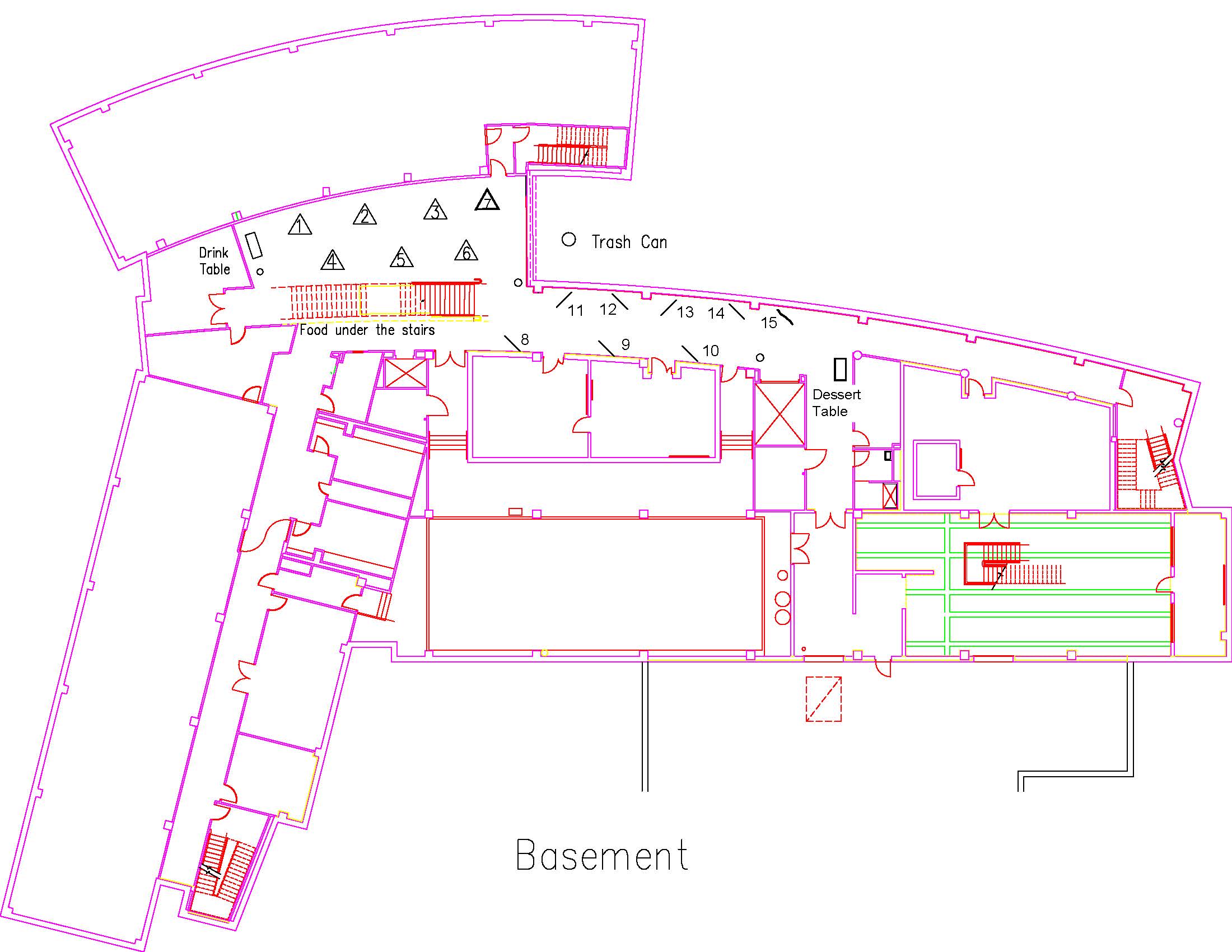
Location: Session: 2; Basement; Table Number: 9
View PresentationThis is experiment is designed to test how Nylon 6-10 is constructed and responds in a microgravity environment. Nylon 6-10 is a very flexible fiber. It consists of two chemicals called polypropylene and sebacoyl chloride to make the nano-structure for Nylon 6-10. We have developed several of ideas on what will happen to Nylon 6-10 in micro-gravity. We think that it will change the molecular structure of the Nylon 6-10 in micro-gravity for the better or worse. The good variable is that Nylon 6-10 might change into a very flexible, durable substance for many different applications both on Earth and in space. One concern we have is that Nylon 6-10 might change the molecular structure to not form any fibers or it might not dry by absorbing air molecules.
We decided to use Nylon 6-10 because of its overall construction. The industrial process for Nylon 6-10 is stronger and more flexible than Nylon 6-6. It is basically liquid rope. It can be used for repairs and manufacturing. It is an industrial chemical. A variety of products are created using Nylon 6-10, toothbrushes, paint brushes and even your underwear. It is a very common product in many of different industries and is a very useful product. It behaves like nylon fiber for thread or can be used for manufacturing different tools such as epoxy or fiberglass. The industrial ideas are very extensive and there are many suppliers.
CHEM2019CAREY22340 CHEM
Synthesis of Heterodimeric Macrocycles
Type: Undergraduate
Author(s):
Hannah Carey
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Jason Mars
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Advisor(s):
Eric Simanek
Chemistry & Biochemistry
Location: Session: 1; 2nd Floor; Table Number: 5

(Presentation is private)Recent trends in drug discovery research are directed at targeting protein-protein interactions. Blocking these interactions could be an effective strategy for treatment. Here, the synthesis of a macrocycle, a large ring-shaped molecule that is the same size as many protein-protein interaction sites, is described. The synthesis relies on the preparation of two different, crescent-shaped molecules through short, multistep syntheses. When these two molecules are combined together and subjected to acid to reveal reactive groups, a spontaneous assembly process occurs. The macrocycle is characterized by conventional methods including 1H NMR (which reveals a diagnostic signal for cyclization), 13C NMR, and mass spectrometry.